Lab 5: Binary Trees and Bitwise Operations
Preliminaries
You will need your notes from class about binary trees and bitwise operations.
This week you will be writing your code in the files called lab5.c, bst.c and bst.h.
Part 1 - Binary Strings to a Short
Write a function called covertToShort inside your lab5.c file that has the following header:
unsigned short convertToShort(char * binString)
This function converts a binary string, which will consists of 16 characters that will be either '1' or '0', into its positive short representation.
E.g.:
char * binStr1 = "0000000000000110"; char * binStr2 = "0000000000000000"; checkit_int(convertToShort(binString),6); /* PASSES */ checkit_int(convertToShort(binString),0); /* PASSES */
Part 2 - Binary Search Tree Library
Create a binary search tree library (i.e. bst.h and bst.c) where each node has a positive short integer value (i.e., unsigned short) as its data value for each node.
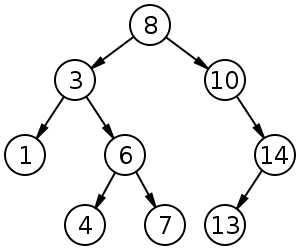
For example:
The above image is an example of a BST that needs to be created where each data value for a node is an unsigned short. Refer to your notes for creating the struct for a binary search tree.
The following functions need to be implemented in your library:
/* Adds a postive short value to the tree */ BST * bst_insert(BST *tree, unsigned short newValue); /* Prints all the nodes in the order (i.e. from smallest value in tree to the largest value in order). Each value should be followed by a newline. */ void bst_traverseInOrder(BST * tree); /* returns "True" (i.e. 1) if findMe is located somewhere in the tree, otherwise "False" (i.e. 0). */ int bst_isValueInTree(BST * tree, unsigned short findMe);
An example of calling the bst_travesInOrder on the tree in the image above should print the following:
1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
Make sure to test your functions in your binary search tree inside the lab5.c file.
Part #3: Putting it All Together
In addition to your previous test cases, create a program inside your lab5.c file that performs the following:
- Reads in a file that contains binary strings (i.e. 16 characters) on each line. There is only one binary string per line.
- The program should convert each binary string into its positive short representation and add the number to a binary search tree.
- Include a few test cases to check to see that numbers you expect to be in the tree are actually in the tree.
- After converting all the binary strings and adding them to the tree, print the tree in order.
Once completed, commit all files to your repository.0000000000001000 0000000000001010 0000000000001110 0000000000001101 0000000000000011 0000000000000001 0000000000000110 0000000000000100 0000000000000111
You have completed the lab! Call me over to show me your lab for credit.